The vast majority of lighting fixtures we see in our daily lives now have LED lights inside, and more and more other lighting systems start using LEDs. LED lights have also become an important part of our daily lives, such as led street light, Building lighting, but what are LED lights and how do LED lights work? Let’s explore together below.
What is LED?
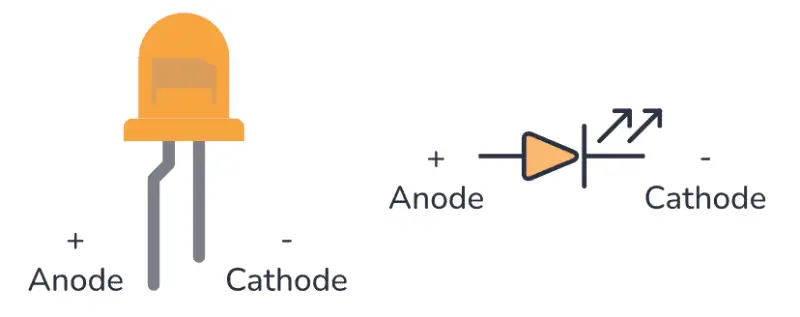
LED (Light Emitting Diode) is a semiconductor component that can convert electrical energy into light energy. The core component of LED is a semiconductor material that can emit light, which is encapsulated on a lead frame.
How do LED Lights Work?
The main principles of LED light emission are the transistor effect and emission radiation effect. By adding a forward voltage at both ends of the LED, the transistor effect and emission radiation effect occur during the process of electron migration, converting electrical energy into light energy.
Transistor effect
The core of LED is composed of semiconductor materials, and the most commonly used semiconductor materials are gallium arsenide and arsenic nitride. The combination of special impurities and these semiconductor materials results in the formation of N-type and P-type regions inside the semiconductors. The junction between N-type and P-type regions forms a P-N junction. When adding a forward current to both ends of the LED, electrons transfer from the N-type region to the P-type region, and holes transfer from the P-type region to the N-type region. When electrons and holes meet at the P-N junction, recombination occurs, and the energy of electrons transfers in the form of light, producing light.
Emission radiation effect
During the process of LED light emission, radiation is generated. When electrons move from the N-type region to the P-type region, they pass through the P-N junction. Due to the special structure of the P-N junction and the band structure of the material, the energy level of the electrons decreases, forming a band difference. The energy level of the electrons decreases, and the kinetic energy decreases. The energy level difference of the electrons will radiate in the form of photons, emitting light.
What gives LEDs their color?

Since the invention of LED, experts have found a large number of semiconductor materials. LEDs using different materials also emit different colors of light. Common materials that will be used to produce different colors include:
- Gallium arsenide (GaAs): Red, red orange, orange yellow, and yellow LEDs
- Phosphorus arsenide (GaP): Red and yellow LEDs
- Nitrogen arsenide (GaN) : Blue and green LEDs
- Silicide: Blue, green, and white LEDs
- Aluminum nitride (AlN): Blue, green, and white LEDs
- Aluminum phosphide (AlP): Blue and white LEDs
There are two primary methods to produce white light. The first is by mixing primary colors (RGB method) where experts combine red, green, and blue LEDs to create white light. The other method uses phosphor coatings where a blue or UV LED excites phosphors to emit broad-spectrum white light. The second method is the more common approach used in household LED bulbs due to its higher efficiency and simpler implementation.
Do LED lights get hot?
LEDs efficiently use energy compared to incandescent bulbs yet generate heat mainly at the junction area. However, they have especially designed heat dissipation methods, which include:
- Heat sinks: Metal components such as aluminum function to extract heat generated from the LED chip.
- PCB design: The circuit boards installed in SMD LEDs function to manage heat distribution in a more effective way.
- Thermal paste: Improves conduction between the LED and heat sink.
How do LED lights get power?
LEDs need specific driver circuits to perform because they are current-dependent devices which require consistent current flow for brightness operation and color stabilization. Most household LEDs use an AC/DC driver to convert alternating current (AC) to low-voltage direct current (DC).
How are leds made?
The main raw materials for LED lights
- The semiconductor materials we mentioned above for different color
-
Substrate Materials:
• Sapphire (most common for GaN LEDs)
• Silicon
• Zinc oxide
• Glass (for flexible LEDs) -
Phosphor Materials:
• Yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG) – Common yellow phosphor
• Silicate-based phosphors
• Nitride-based phosphors -
Other Essential Materials:
• Gold or copper wire bonding
• Silver epoxy adhesives
• Aluminum heat sinks
• Epoxy or silicone encapsulation
• Ceramic or plastic packages
The manufacturing process of raw materials for LED lights
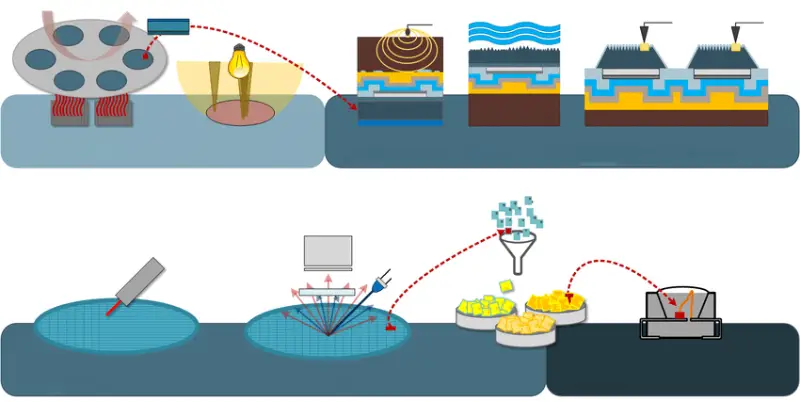
Growth substrate
The manufacturing process of LED lights usually starts from the growth substrate. The growth substrate can be prepared by methods such as melting and vapor deposition to provide high-quality substrate materials.
Substrate surface treatment
Surface treatment on growth substrates typically involves processes such as removing impurities and oxides to improve the quality and efficiency of LED chips.
Material epitaxy
Material epitaxy refers to the growth of another layer of semiconductor material on a growth substrate after surface treatment to form the structure of LED chips. The epitaxial process usually uses techniques such as chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or molecular beam epitaxy (MBE).
Preparation of electrodes
Electrodes can provide current transfer and light radiation. After completing the material epitaxy, experts make electrodes through metal film deposition and electroplating.
Solid crystal
After preparing the electrodes, it is necessary to solidify the LED chip on the substrate to provide stable support and protection. Solidification is usually carried out using adhesives or welding techniques.
encapsulation
After the solidification is completed, the LED chip needs to be packaged to protect and integrate the chip. Encapsulation includes processes such as bracket installation, cable connection, and epoxy resin encapsulation.
Testing and packaging
After the packaging process, it is necessary to perform functional and quality testing on the LED lights to ensure their performance and reliability. Through good testing and packaging, the quality and service life of LED lights can be guaranteed.




