A well-lit parking lot provides bright and even lighting, helps reduce accidents and theft, and keeps parking lots safe. To achieve this, a comprehensive approach to parking lot lighting design is essential. With appropriate lighting design and parking lot lights selection, you can illuminate your parking area in a way that feels bright and welcoming to all users. This detailed tutorial discusses the most important aspects to consider when designing parking lot lighting.
1. HID vs LED
Many traditional HID lights used in street and parking lot lighting are now considered outdated and are being replaced by modern LED lights. HID lights are not energy efficient, using mostly electrical power to generate light. They will produce uneven lighting with both bright and dark spots across the lot, reducing visibility and indirectly increasing safety issues and crime risk after hours. The bright spots also cause light pollution and glare. HID lamps have a relatively short lifespan and require frequent replacement. LED street lights, on the other hand, consume less power with more light output. They allow precise lighting control through adjustable optics and emission patterns. This means less energy is wasted on unnecessarily bright or misdirected light. The uniform lighting improves visibility evenly throughout the lot. LEDs last up to ten times as long as HIDs and require less maintenance during their lifetime.
2. Light distribution design
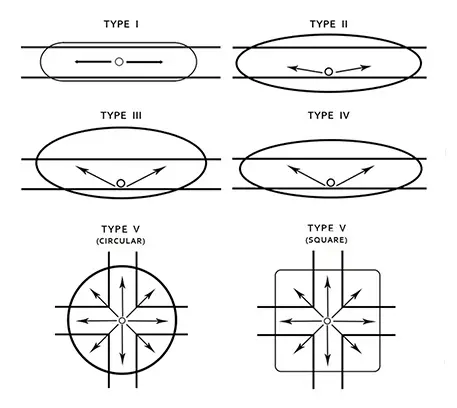
Among the common light distribution types for parking lot fixtures, types III, IV, and V are usually suitable. Type III luminaires emit light outward at a wide angle. They are ideal for installing along the perimeter of the lot to illuminate the surface area. Type IV produces semicircular or half-circle distribution from wall mounts or building sides. For very large commercial parking areas with a need to light the center, type V full-circle distribution provides consistent brightness in all directions from the fixture. It is also important that all fixtures use cut-off or semi-cut-off lights to prevent light overflow. Uncontrolled light direction can lead to light pollution and glare, which can negatively affect the night sky, disrupt the nocturnal activities of animals, and impact human circadian rhythms.
3. Uniformity of light
According to a study conducted by Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute’s Illumination Research Center (LRC), enhancing the uniformity of parking lot illumination can boost perceived safety. At present, many parking facilities simply rely on high-mast lights for broad coverage using a few fixtures. However, this results in uneven surface illumination with wide variations, deep shadows behind vehicles, and dimly lit areas further from poles. The study found that through strategic lighting design and selection of lights, the uniformity of illumination is significantly improved when more ordinary street light poles are arranged.
4. How bright should the parking lot lights be?
As a general guideline, the average illumination of the horizontal surface area of a parking lot should be at least 20 to 50 lux (2-5 foot-candles). This level provides enough light to improve vehicle safety when approaching and exiting the parking lot. For parking lots with heavy traffic, areas with high crime rates, or specific areas such as railings, entrances, and exits, the lighting should be appropriately enhanced to at least 50 lux. Typically, the supplier can recommend parking lot lights of appropriate specifications once they are informed of the parking lot’s area.



5. Height and spacing of parking lot lights
Most parking lot lights are built at heights ranging from 12 to 20 feet, with some reaching 35 feet. Taller street lights can provide lighting for a wider area. But if the surrounding area is a residential area, excessively high street lights can affect people’s rest at night. Conversely, the excessive pursuit of large-area lighting with high light poles leads to a waste of resources. But you will need more lower street lights than the higher ones to achieve the required level of illumination. This may increase energy consumption and maintenance costs. Typically, the height of the light poles should range from 0.7 to 1 times the width of the illuminated road. The spacing between light poles should be about 2.5 to 3 times the height of the light poles. You can use our calculator to decide the spacing and height of your lights!
6. Color temperature of parking lot lights
Color temperatures for parking lot lights commonly range from 4000K to 5000K. Compared to the warmer yellow tones of 3000K lighting, the 4000K-5000K range provides a cooler color, closer to natural light. In a dark night environment, this type of light can increase people’s alertness, help them identify potential dangers more quickly, and enhance their sense of security. A color temperature of 5000K also provides higher visual contrast, which is important for distinguishing different objects, identifying vehicle colors, and improving people’s perception of their surroundings.
7. How are parking lot lights controlled?
There are also various lighting control strategies that enable flexibility and optimize energy savings for parking facilities. Photocell sensors automatically activate fixtures after dusk and switch them off at dawn based on natural sunlight conditions for set-and-forget operation. Alternatively, an astronomical time clock circuit can be programmed to factor in local sunrise and sunset timing adjustments throughout different seasons.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is essential to consider a range of factors, including light source selection, light distribution design, uniformity, brightness, height and spacing, color temperature, and control methods, when designing parking lot lighting. Common parking lot lighting issues, such as uneven and dim lighting, can significantly impact the perceived safety of the area and discourage customers from utilizing the parking facility. Therefore, it is crucial to design a suitable parking lot lighting solution and engage with a reliable manufacturer like us who can provide the best solution. Talk with us right away!




